What Are Some Similarities In Restraining Small And Large Animals
Human and animal skeletons are two types of hard structures in the torso whose principal function is to provide structural support while aiding locomotion. Even so, at that place are some similarities and differences between human and animate being skeletons. Humans are vertebrates and have an endoskeleton fabricated upwardly of bones and cartilage. Meanwhile, other animals like arthropods accept an exoskeleton and invertebrates have a hydrostatic skeleton. Furthermore, the growth of the endoskeleton stops at maturity while arthropods shed their exoskeleton several times during their lifetime.
Central Areas Covered
i. What is Homo Skeleton
– Definition, Facts, Construction
two. What is Animal Skeleton
– Definition, Types, Office
3. What are the Similarities and Differences Between Human and Animal Skeletons
– Outline of Common Features and Comparison of Key Differences
Primal Terms
Creature Skeleton, Backbone, Endoskeleton, Exoskeleton, Human Skeleton, Hydrostatic Skelton, Skull
What is Human Skeleton
Human skeleton is the structural framework of humans. Therefore, its principal function is to provide structural support to the trunk. Also, it aids in the movement of the body. Since human being skeleton occurs within the torso, it is an endoskeleton. The human skeletal system contains bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles.
Bones
Basic are a strong tissue, which is lightweight. They are able to abound and repair themselves. The periosteum or the outer layer of bones contains both fretfulness and blood vessels. Hard, meaty bones occur beneath the periosteum. Calcium phosphate and collagen fibers are the structural components of these compact bones. The key office of the os is made up of spongy bones, which are soft and porous.
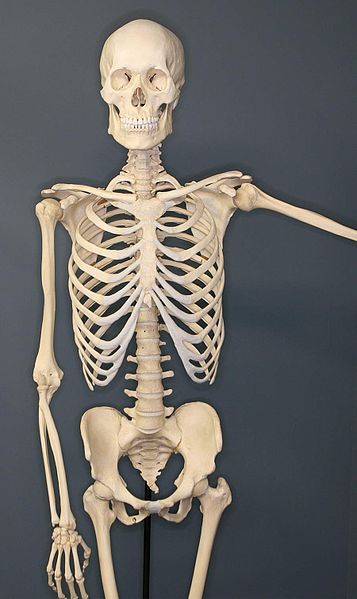
Figure 1: Man Skeleton
Human skeleton consists of 206 bones, grouped into long bones, brusk basic, apartment bones, and irregular bones. At birth, it contains effectually 270 bones, just this number gets reduced past machismo with the fusion of some bones. Some of the main bones in the homo skeleton are skull, vertebral cavalcade, ribs, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, pelvis, femur, tibia, etc.
Joints
A joint or an articulation is a place where two basic meet in the body. Shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, ankles, and knees are some of the major joints in the homo skeleton. Moreover, they aid the move of bones by assuasive bones to pin, twist, rotate, hinge, or slide. In synovial joints, bones articulate by means of a cartilage. Moreover, these joints contain a cavity filled with a fluid.
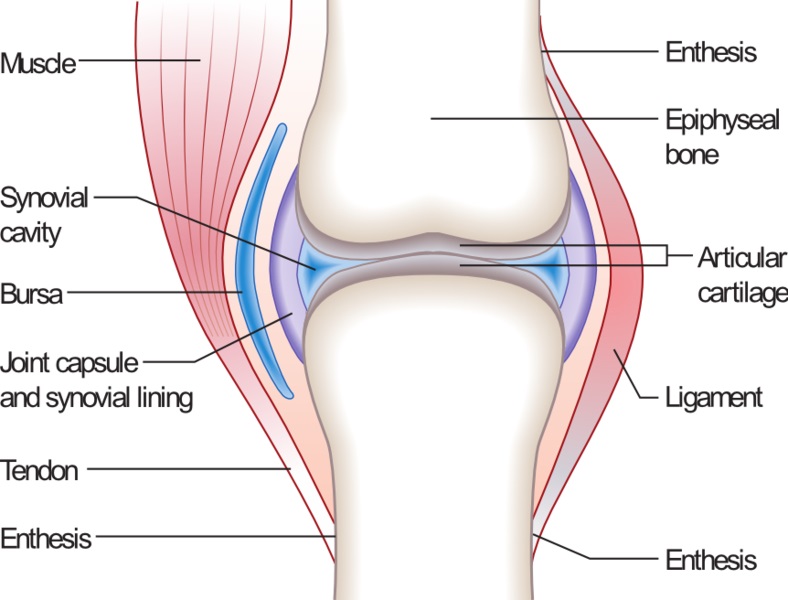
Effigy ii: Joint
Ligaments
Ligaments are bands of gristly connective tissue, which hold bones or cartilages together in a articulation.
Muscles
Muscles are bundles of fibrous tissue with the power to contract. Along with bones, they produce voluntary movements. Here, muscles attach to the basic through a tendon.
What is Brute Skeleton
Animate being skeleton is the structural framework of animals. Based on the construction, three types of skeletons occur in animals: endoskeletons, exoskeletons, and hydrostatic skeletons.
Endoskeleton
Endoskeleton is the internal skeleton fabricated up of bones and cartilages. Information technology occurs inside the body of vertebrates, including humans, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Moreover, it develops from the endoderm and is a living construction. It grows as the body grows and a single skeleton is maintained throughout the lifetime of the animal.
Figure iii: Endoskeleton
The two primary parts of the endoskeleton are axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton consists of the skull and backbones. The master function of the skull is to protect the brain. Backbone protects the spinal cord. The appendicular skeleton provides support to the appendages while protecting internal organs.
Though the primary role of the endoskeleton is to provide structural support and assist in the movement, it also involves in the protection of internal torso organs. In add-on, it produces blood cells in a process chosen hematopoiesis. Also, the os matrix serves as a storage compartment of calcium, fe, ferritin, and phosphate. In addition, bone cells perform an endocrine office past secreting hormones similar osteocalcin, which regulates blood sugar levels and fat deposition.
Exoskeleton
Exoskeleton is the external skeleton of arthropods; it is made upwards of chitin. It occurs in diplopods, chilopods, arachnids, crustaceans, and insects. The principal feature feature of the exoskeleton is its molting. Arthropods have to shed their skeleton since it occurs outside the body and prohibits the growth of the body. Therefore, they develop several exoskeletons during their lifetime. In addition, mollusks accept an exoskeleton made up of calcium compounds. Nevertheless, they do non shed their skeleton.

Figure 4: Exoskeleton
Hydrostatic Skeleton
Hydrostatic skeleton is a fluid-filled compartment within the body called coelom. Hither, hydrostatic force per unit area is the main factor which provides structural back up. Also, it supports the internal organs. This is institute in invertebrates with soft bodies similar body of water anemones, earthworms, and cnidarians.
Figure 5: Hydrostatic Skeleton
What are the Similarities and Differences Between Homo and Animal Skeletons
The post-obit department looks at both similarities and differences between human and brute skeletons.
Similarities Between Human and Animal Skeletons
- Homo and animal skeletons are two types of hard structures which provide structural support to the body.
- They also assist in locomotion.
- Both types of skeletons grow in size with time and reach a steady land.
- Humans are vertebrates, who have an endoskeleton fabricated upwardly of bones and cartilage.
- The ii principal parts of the vertebrate skeleton are the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
- Skull and courage are the 2 master parts of the axial skeleton. Meanwhile, the appendicular skeleton protects the internal organs while providing structural support and the aiding the movement.
- Most vertebrates and humans share basic bones and muscles just in different proportions and ratios.
Deviation Between Man and Animal Skeletons
Definition
Human skeleton refers to the internal framework of the human body, composing of 206 bones, while fauna skeleton refers to a usually rigid supportive or protective structure or framework of an organism.
Types of Skeletons
The human being skeleton is an endoskeleton while vertebrates have an endoskeleton, arthropods have an exoskeleton, and invertebrates have a hydrostatic skeleton.
Growth of the Skeleton
The growth of the endoskeletons similar human skeleton stops at some point and maintains a steady country while exoskeleton is shed after the growth.
Conclusion
The man skeleton is an endoskeleton, which occurs inside the body. It resembles most endoskeletons of vertebrates. Other animals similar arthropods have an exoskeleton while invertebrates have a hydrostatic skeleton. Moreover, both human and animal skeletons are two types of hard structures which provide structural support to the body, while aiding in locomotion. These are the primary similarities and differences between human being and animal skeletons.
References:
i. "Types of Skeletal Systems|Boundless Biology."Lumen Learning, Lumen, Available Hither
Image Courtesy:
1. "Human-Skeleton" By Sklmsta – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. "Joint" Past Madhero88 – Ain piece of work Info sites i ii 3 (CC BY-SA iii.0) via Commons Wikimedia
3. "Types of Skeletal Systems" By OpenStax College (CC By three.0) via OpenStax CNX
4. "Gecarcinus quadratus (Nosara)" By (Bhny) – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prototype:HalloweenCrab.JPG (Public Domain) via Eatables Wikimedia
v. "Types of Skeletal Systems" By OpenStax College (CC Past iii.0) via OpenStax CNX

Source: https://pediaa.com/what-are-the-similarities-and-differences-between-human-and-animal-skeletons/
Posted by: yinglingcurness.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are Some Similarities In Restraining Small And Large Animals"
Post a Comment